Advanced Cardiac Device Implantation: Pacemakers, ICDs, and CRT Procedures
Pacemakers, Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs), and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) devices are all crucial in managing various heart conditions. Here’s a breakdown of each:
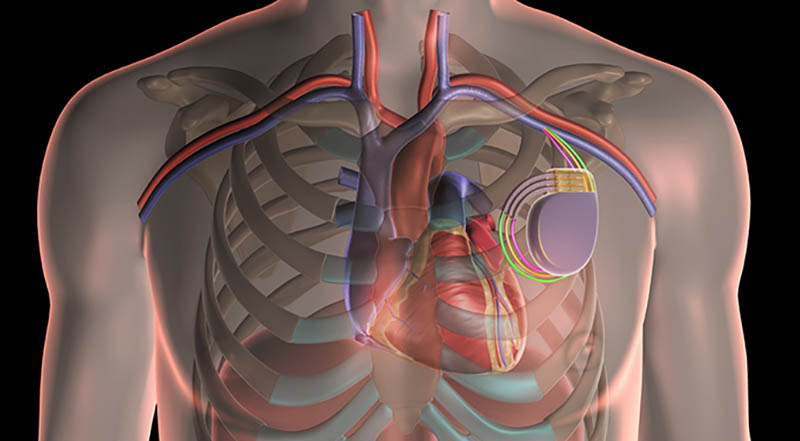
- Pacemakers: These are small, battery-operated devices that are implanted under the skin, usually near the collarbone. They are used to treat arrhythmias, which are irregular heartbeats. Pacemakers work by sending electrical impulses to the heart to help it maintain a normal rhythm. They can also monitor the heart’s electrical activity and adjust the pacing as needed.
- Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs): Like pacemakers, ICDs are also implanted under the skin, typically near the collarbone. However, their function is different. ICDs continuously monitor the heart rhythm and deliver electric shocks to restore a normal rhythm if a dangerous arrhythmia, such as ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia, is detected. These shocks can be lifesaving for individuals at risk of sudden cardiac arrest.
- Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT): This therapy is often used for individuals with heart failure and certain types of arrhythmias. CRT involves the implantation of a special pacemaker that sends electrical impulses to both the left and right ventricles of the heart, helping them to beat in a more synchronized manner. By coordinating the heart’s contractions, CRT can improve symptoms, exercise capacity, and overall quality of life for individuals with heart failure.
Implantation procedures for these devices are typically performed by cardiologists or electrophysiologists in a hospital setting. The procedures are generally safe but, like any medical intervention, carry some risks, such as infection or bleeding. Following implantation, regular follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor device function and adjust settings as needed.
It’s important for individuals with these devices to be aware of any restrictions or precautions related to activities or environments that could interfere with the function of the device, such as certain types of electromagnetic fields or security scanners. Additionally, they should be educated on how to recognize and respond to any symptoms or alerts from their device.